Generally speaking, power banks are manufactured using two main types of rechargeable batteries: Lithium-ion and Lithium-polymer. And of the two, Lithium-ion power banks are the most common ones. However, Lithium-polymer power banks have been recently gaining ground in the market.
The two main questions customers have regarding Lithium-ion and Lithium-polymer power banks are “How different do they perform?” and especially “Which one is better?“. Judging from our experience, there’s too much confusion concerning this topic. To clear it up, we are exploring and comparing the main differences between Lithium-ion and Lithium-polymer portable chargers.
Learning About Lithium-ion and Lithium-polymer Batteries
 Let’s begin with the basics, what’s exactly a lithium-ion battery?
Let’s begin with the basics, what’s exactly a lithium-ion battery?
According to Battery University, a free educational website offering hands-on battery information, the lithium-ion battery, or Li-ion, was conceived in the early nineties as an answer to safety concerns over rechargeable metallic lithium batteries. Sony first commercialized it in 1991, and since then, it has become the most widely used battery in the electronic market.
There are four main components of Li-ion batteries:
- The cathode, which is the source of lithium ions, determines the capacity and the average voltage.
- The anode, stores and releases the lithium ions from the cathode.
- The electrolyte is a liquid chemical compound that allows the movement of ions.
- The separator prevents contact between the anode and cathode.
On the other hand, lithium-polymer batteries, also known as LiPo, have evolved from Li-ion batteries and follow the same design. For making the battery conductive at room temperature, nowadays, the type of electrolyte in the manufacturing of most LiPo cells is a gel, while a microporous separator replaces the traditional one.
The Difference Between Li-ion and LiPo Power Banks
As expected, the change in electrolytes results in slight differences between one another.
On the one hand, Li-ion cells usually have a low manufacturing cost, and while they have a limited mAh capacity, they tend to last longer as they don’t have the memory effect. This phenomenon occurs when the battery experiences losses in usable capacity from charging-discharging and recharging over time.
On the other hand, LiPo cells are made thinner and lighter, to the point of resembling a credit card, and can store slightly higher specific energy than Li-ion ones, but they’re more expensive to manufacture. Besides, they do suffer from the memory effect and have shorter lifespans.
So how does this translate to power banks?
The following table summarizes the most significant differences between Li-ion and LiPo power banks:
[table id=4 /]Which Ones Are Better?
As the table shows, the main advantage of power banks with LiPo batteries is that they’re more compact and lightweight. Besides, two of the main features users are looking for in a power bank are how compact it is and how much power it can deliver.
Thus, logically, LiPo batteries offer both of these qualities; in fact, they allow manufacturers to capitalize and play with different shapes and sizes (lipstick, credit card) as well as lightweight, making them more attractive to buyers.
However, despite being less safe, most renowned brands still implement Li-ion batteries due to two main things: low cost and durability. In the long term, users want a power bank that not only looks fashionable, but also feels durable, and Li-ion power banks don’t become harder to recharge with the pass of time as it’s the case of LiPo power banks. In addition, manufacturers can save costs in their production, while offering good quality and as much power as LiPo power banks.
As for the drawbacks, LiPo batteries are more expensive, increasing the total production cost of such power banks, and according to Battery University, “they have identical charge and discharge characteristics to other Li-ion systems, but their foil package may be less durable than Li-ion in the cylindrical package“.
The main disadvantages of Li-ion power banks consist of the fact that they suffer from aging, even when not in use, and carry a certain risk of explosion. The rate of aging can vary depending on various factors, including temperature, storage conditions, and battery management systems.
It’s unfair to say that one type of battery is better than the other when both offer great benefits, as well as minor disadvantages. Overall, LiPo power banks are better for shoppers looking for portability, while Li-ion ones are better suited for those looking for durability.
Which Power Banks Are Safer?
Regarding safety concerns, at first glance, LiPo power banks have improved safety. However, all batteries, regardless of their design, can explode, but they are not hazardous with the right handling and use. Therefore, if you don’t overcharge Li-ion power banks or expose them to harsh conditions, there’s no need to worry about possible combustion, especially when most renowned brands have equipped them with multiprotection systems.
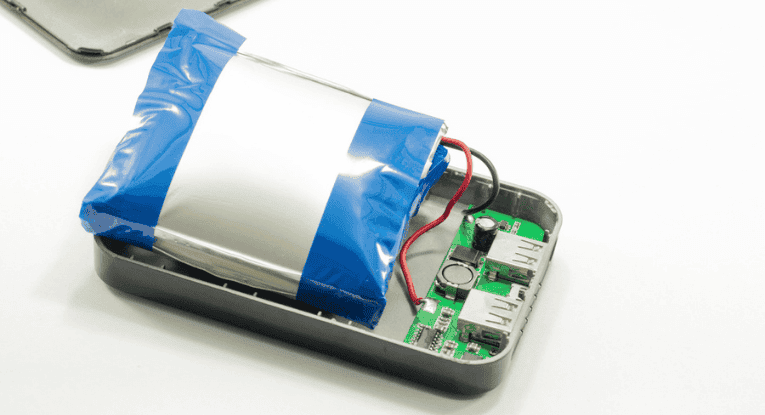
The risk of explosion or combustion varies depending on the battery chemistry, design, manufacturing quality, and usage conditions. It is important to note that lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries are generally considered safe when used properly and manufactured by reputable brands.
For more about this topic, check our past article: “Can power banks explode?“. There you can learn how to choose a power bank with little risk of explosion, how to avoid a fire, and how to identify signs of malfunction that might result in an explosion.
Conclusion
Overall, there isn’t much difference between one type of power bank and the other, particularly regarding their performance. Just make sure that the one you choose meets the requirements of your devices, and that they’re equipped with a solid multiprotection system.
While it’s undeniable that more electronic devices will start incorporating LiPo batteries due to their compact size, big companies will also continue trying to cut down expenses by using Li-ion batteries. For this reason, Li-ion power banks are not going anywhere anytime soon, but the technology is ever-changing so it’s likely to see power banks with a new type of batteries shortly.